| Home Page | |
| FAQ | |
| Publications | |
| Documentation | |
| Software | |
| Movies | |
| Image Gallery | |
| Image Data | |
| Data Search | |
| Derived Products | |
| Related Links | |
| Contact Us | |
| SCP file site | |
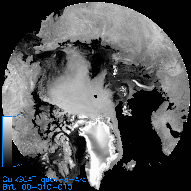
OSCAT Ice Extent Products The OSCAT sea ice extent algorithm is based on an modification of the QuikSCAT algorithm (Remund and Long, 2014). The estimated extent of sea ice is estimated for each Ant and Arc regional image for both slices and eggs. The polarization ratio (AV-AH in dB), incidence angle dependence (B images), and the sigma-0 estimate error standard deviation (V images) are used to perform the sea ice/ocean discrimination. Residual misclassification noise is reduced using binary image processing techniques such as region growing, erosion, and dilation resulting in a low pass filtered version of the sea ice extent edge. The sea ice extent product is in two forms: a masked image generated by applying the binary extent mask to the V-pol, A-image (.imsk file) and an ASCII edge file (.ie file). The lat/lon values in the ASCII edge files were obtained by computing the lat/lon location of each pixel along the edge of the binary ice mask. Ice extent products are included in the V-pol, ascending/descending, A image directories of the Antarctic (Ant) and Arctic (Arc) regions for eggs (quev) and slices (qusv).
Masked V-pol files (.imsk): Masked V-pol, A image of quev and qusv images of Antarctica (Ant) and the(Arc). Ocean areas outside of the estimated sea ice extent are set to the no-data value. IE files (.ie): ASCII files containing latitude/longitude pairs which represent the contour points of the estimated sea ice edge. Each line entry in the file consists of two values: a longitude and a lattitude. The longitude values range from -180 to +180. Multiple contours are separated by a '0 0' entry. Reduced size sample masked image product
References: Q.D. Remund and D.G. Long, "A Decade of QuikSCAT Scatterometer Sea Ice Extent Data," IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, doi:10.1109/TGRS.2013.2281056, Vol. 52. No. 7, pp. 4281-4290, 2014. Q.P. Remund and D.G. Long, "Iterative Estimation of Antarctic Sea Ice Extent Using Seawinds Data," Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, pp. 491-493, Hilton Hawaiian Village, Honolulu, Hawaii, 24-28 July 2000. Q.P. Remund and D.G. Long, "Sea Ice Extent Mapping Using Ku-Band Scatterometer Data," Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 104, No. C5, pp. 11515-11527, 1999. Q.P. Remund and D.G. Long, "Sea Ice Mapping Algorithm for QuikSCAT and Seawinds," Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, pp. 1686-1688, Seattle, Washington, 6-10 July, 1998. Related References: H.S. Anderson and D.G. Long, "Sea Ice Mapping Method f or SeaWinds," IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 43, No. 3, pp. 647-657, 2005. J. Haarpainter, R.T. Tonboe, D.G. Long and M. L. VanWoert, "Automatic Detection and Validity of the Sea Ice Edge: An Application of Enhanced Resolution QuikScat/SeaWinds Data," IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 42, No. 7, pp. 1433-1443, 2004. J. Haarpaintner, "Arctic-Wide Operational Sea Ice Drift From Enhanced-Resolution QuikSCAT/SeaWinds Scatterometry and Its Validation," IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 44, No. 1, pp. 102-107, 2006. J. Haarpainter and G. Spreen, "Use of Enhanced-Resolution QuikSCAT/SeaWinds Data for Operational Ice Services and Climate Research: Sea Ice Edge, Type, Concentration, and Drift," IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol. 45, No. 10, pp. 3131-3137, 2007. |